Electrical: Electrical Control Systems specializes
in the design and manufacture of high quality industrial control systems and
offer innovative and practical solutions to all your automation requirements
ranging from simple MCC and dedicated controller applications, to networked PLC
and SCADA systems.
Pneumatic: A system in which gas pressure
differences and their rates of change are related to gas flows, their integrals
and their rates of change.
Hydraulic: A mechanism operated by the resistance
offered or the pressure transmitted when a liquid is forced through a small
opening or tube
System – An interconnection of elements and devices
for a desired purpose.
Control System – An interconnection of components
forming a system configuration that will provide a desired response.
Process – The device, plant, or system under
control. The input and output
relationship represents the cause-and-effect relationship of the process.
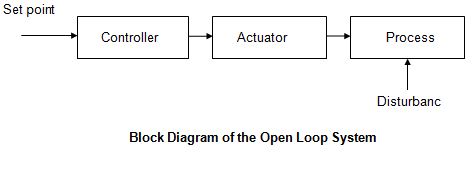
Open-Loop Control Systems utilize a controller or
control actuator to obtain the desired response.
Closed-Loop Control Systems utilizes feedback to
compare the actual output to the desired output response.
Multivariable Control System
Term Used In Control System
Acceleration Error
The amount of steady state error of the system when
stimulated by a unit parabolic input.
Acceleration Error Constant
A system metric that determines that amount of
acceleration error in the system.
Adaptive Control
A branch of control theory where controller systems
are able to change their response characteristics over time, as the input
characteristics to the system change.
Adaptive Gain
when control gain is varied depending on system
state or condition, such as a disturbance
Additivity
A system is additive if a sum of inputs results in a
sum of outputs.
Analog System
A system that is continuous in time and magnitude.
ARMA
Autoregressive Moving Average
ATO
Analog Timed Output. Control loop output is
correlated to a timed contact closure.
A/M
Auto-Manual. Control modes, where auto typically
means output is computer-driven, calculated while manual can be field-driven or
merely using a static setpoint.
Bilinear Transform
a variant of the Z-transform,
Block Diagram
A visual way to represent a system that displays
individual system components as boxes, and connections between systems as
arrows.
Bode Plots
A set of two graphs, a "magnitude" and a
"phase" graph, that are both plotted on log scale paper. The
magnitude graph is plotted in decibels versus frequency, and the phase graph is
plotted in degrees versus frequency. Used to analyze the frequency
characteristics of the system.
Bounded Input, Bounded Output
BIBO. If the input to the system is finite, then the
output must also be finite. A condition for stability.
Cascade
When the output of a control loop is fed to/from another loop.
Causal
A system whose output does not depend on future
inputs. All physical systems must be causal.
Classical Approach
See Classical Controls.
Classical Controls
A control methodology that uses the transform domain
to analyze and manipulate the Input-Output characteristics of a system.
Closed Loop
a controlled system using feedback or feedforward
Compensator
A Control System that augments the shortcomings of
another system.
Condition Number
Conditional Stability
A system with variable gain is conditionally stable
if it is BIBO stable for certain values of gain, but not BIBO stable for other
values of gain.
Continuous-Time
A system or signal that is defined at all points t.
Control Rate
the rate at which control is computed and any
appropriate output sent. Lower bound is sample rate.
Control System
A system or device that manages the behavior of
another system or device.
Controller
See Control System.
Convolution
Convolution
A complex operation on functions defined by the
integral of the two functions multiplied together, and time-shifted.
Convolution Integral
The integral form of the convolution operation.
CQI
Control Quality Index,
CV
Controlled variable
Damping Ratio
A constant that determines the damping properties of
a system.
Deadtime
time shift between the output change and the related
effect (typ. at least one control sample). One sees "Lag" used for
this action sometimes.
Digital
A system that is both discrete-time, and quantized.
Direct action
target output increase is required to bring the
process variable (PV) to setpoint (SP) when PV is below SP. Thus, PV increases
with output increase directly.
Discrete magnitude
See quantized.
Discrete time
A system or signal that is only defined at specific
points in time.
Distributed
A system is distributed if it has both an infinite
number of states, and an infinite number of state variables. See Lumped.
Dynamic
A system is called dynamic if it doesn't have
memory. See Instantaneous, Memory.
Eigenvalues
Solutions to the characteristic equation of a
matrix. If the matrix is itself a function of time, the eigenvalues might be
functions of time. In this case, they are frequently called eigenfunctions.
Eigenvectors
The nullspace vectors of the characteristic equation
for particular eigenvalues. Used to determine state-transitions, among other
things.
Euler's Formula
An equation that relates complex exponentials to
complex sinusoids.
Exponential Weighted Average (EWA)
Apportions fractional weight to new and existing
data to form a working average. Example EWA=0.70*EWA+0.30*latest, see
Filtering.
External Description
A description of a system that relates the input of
the system to the output, without explicitly accounting for the internal states
of the system.
Feedback
The output of the system is passed through some sort
of processing unit H, and that result is fed into the plant as an input.
Feedforward
whwn apriori knowledge is used to forecast at least
part of the control response.
Filtering (noise)
Use of signal smoothing techniques to reject
undesirable components like noise. Can be as simple as using exponential
weighted averaging on the input.
Final Value Theorem
A theorem that allows the steady-state value of a
system to be determined from the transfer function.
FOH
First order hold
Frequency Response
The response of a system to sinusoids of different
frequencies. The Fourier Transform of the impulse response.
Fourier Transform
An integral transform, similar to the Laplace
Transform, that analyzes the frequency characteristics of a system.

No comments:
Post a Comment