Wednesday, 31 July 2013
Tuesday, 30 July 2013
formula for chapter 2
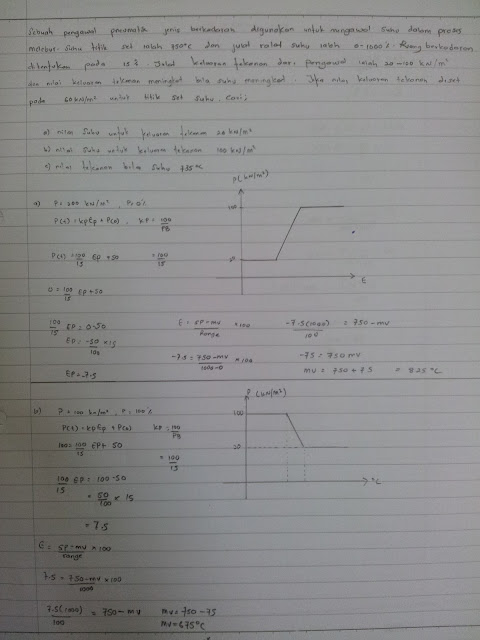
- CONTROLLER OUTPUT IN PERCENT.
Controller output % = current output - minimum output X 100
maximum output - minimum output
- MEASURE VALUE AS PERCENTAGE
Measure value in % = MV - minimum MV X 100
max MV - minimum MV
- SET POINT AS PERCENTAGE VALUE
Set point % = SP - min value X 100
max value - min value
- ERROR AS PERCENTAGE VALUE
Error point % = % SP X MV X 100
max value - min value
- PROPORTIONAL BAND
Proportional band , PB = 100
proportional gain , KP
PB = 100
KP
- CONTROLLER OUTPUT
P = Kp*Ep X P(0)
- POSITIVE ERROR BAND
Positive error band = max permissible positive error X100
temp range
- NEGATIVE ERROR BAND
Negative error band = max permissible negative error X100
temp range
- PROPORTIONAL CONTROLLER
E = SP - MV
P(i) = KP*EP + P(0)
Tuesday, 23 July 2013
CHAPTER 2
PRINCIPLES
OF CONTROLLERS
2.0 EXPLANATION
OF PRINCIPLES OF BASIC CONTROLLERS
The main component of controller are :
a) Comparator
mechanism
b) Controller
c) Feedback
mechanism
Controller is a
device which receives input from two points :
(i)
a value which is sent by transmitter
(ii)
a value which is set by set point
The output from
the controller is send to the valve controller.
Figure
2.0 : Block Diagram of controller
Figure
2.0 shows the input controller is a signal which is sent by transmitter. This
signal is known as a transmitter signal (MV) and set point. If the output
depends on the two inputs functions well and the process is in a stable
condition, then the transmitter signal is similar to the set point. The comparator mechanism functions as comparator
of both input signals. An error will exist if the input value is not the same.
The detector will detect the error signal and determine if there is imbalance
between error signal and feedback signals. If there is a difference, the
detector will balance both of these signals. The feedback mechanism is a
mechanism which balances the system. The feedback signal is always similar to
the output signal.
The main components of controller
are :
(i)
Comparator mechanism. It consists of two bellows which is
for transmitter signal and set point signal. Its function is to differentiate
both the input signals.
(ii)
The controller consists of a flapper and nozzle. Its
function is to detect the error signal from the different output and the
feedback signal.
(iii)
The feedback mechanism consists of the feedback bellows. Its
function is to balances and stable the system. It also has an effect towards
multiple output of a controller.
2.1 EXPLANATION
OF BASIC CONTROLLERS COMPONENTS
2.1.1
Bellows
The structure of a bellow is shown in Figure 2.1. It consists of a thin metal which is formed into a wave cylinder shape. Air pressure will depress a bellow. When air pressure is increased, bellow will extend and displacement exists. This displacement is linked to the convenient‘lever’ for give the pressure increase reading. This displacement force include in mechanical force categories.
2.1.2 Flapper Nozzle
Flapper nozzle is a displacement
transducer which the displacement into a differential pressure parameter.
Figure 2.2 shows a structure of flapper nozzle. Basically air is used as work
liquid. Air will give a constant time about 0.1s. Flapper nozzle is used for
measuring of displacement between load cell. This displacement is very small.
Figure 2.2 :
Flapper Nozzle
2.1.3 Restrictor
Accuracy of an
instrument is guaranteed by manufacturers only for a certain limit. Normally it
is stated in the form of a full scale percent of that particular instrument.
Deflection from the specification is called restrictor error.
2.2 DESIGN OF
SCHEMATIC CIRCUIT FOR CONTROLLER ACTION TYPES
There
are three types of controller :
a) Proportional
controller
b) Integral
controller
c) Derivative
controller
2.2.1 Types of Controller
There are a few types of controller
used to control a process either in a form of Proportional output to the error,
Proportional and Integral to the error or Proportional and Derivative output to
the first error.
Controller can be used in the form
of single mode of Proportional, Integral, or Derivative, two mode of
Proportional and Integral (P+I) and Proportional and Derivative (P+D), and
three mode of Proportional, Integral and Derivative (P+I+D).
The
figures below show the design of schematic circuit for controller action types.
(i) Proportional Controller (P)
(iii)
Integral Controller
(iv)
Derivative Controller (D)
(v)
Proportional + Integral + Derivative Controller (P+I+D)
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)